A new report from cybersecurity leader WatchGuard Technologies reveals a significant surge in sophisticated cyber threats, with attackers increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to power their campaigns. However, the report also highlights the growing effectiveness of AI and machine learning (ML) powered security solutions in detecting and neutralising these advanced threats.
WatchGuard’s latest Internet Security Report for Q1 2025 shows a staggering 171% increase in total unique malware detections quarter-over-quarter, the highest recorded by the WatchGuard Threat Lab. This surge is attributed mainly to a sharp rise in “zero-day malware” – evasive threats designed to bypass traditional, signature-based security systems.
“The latest findings in the Q1 2025 Internet Security Report seem to support a larger cybersecurity industry trend: the AI war is here,” said Corey Nachreiner, Chief Security Officer, WatchGuard Technologies. “Attackers now have the capabilities to launch highly targeted campaigns at scale using automated pipelines, emphasising the need for organisations to adopt robust, precise, and powerful security measures to stay ahead of the advancements in AI and the evolving cyber risks.”
Key Findings from the Q1 2025 Report:
AI-Powered Defence is Critical for Evasive Threats: WatchGuard’s IntelligentAV (IAV), a proactive AI and machine learning detection service, saw a remarkable 323% increase in malware detections. This highlights the crucial role of advanced AI/ML in detecting complex, previously unseen malware that traditional antivirus solutions often miss.
Encrypted Channels Remain a Top Attack Vector: Malware delivered over encrypted (TLS) connections increased by 11 points in Q1, now accounting for 71% of all detections. This underscores the continued reliance of attackers on obfuscation and encryption to conceal their malicious activities.
New Endpoint Malware Surges Dramatically: While overall endpoint malware volume decreased, new and unique malware threats on endpoints exploded by 712% this quarter. This significant jump signals a shift in attacker tactics towards constantly evolving malware variants.
LSASS Dumper Leads Endpoint Threats: The most prevalent malware threat detected on endpoints was LSASS dumper, a credential stealer. This tool exploits a critical Windows security process to gain access to sensitive information like passwords and access tokens.
Ransomware Landscape is Shifting: Ransomware detections declined by 85% from the previous quarter , aligning with an industry trend away from crypto ransomware. Threat actors are increasingly focusing on data theft rather than encryption, likely due to improvements in data backup and recovery strategies. However, Termite ransomware, a new group, was still the second most detected malware threat.
Attack Vectors Evolve: Historically, malicious scripts have been the primary attack vector for endpoint malware detection. In Q1, script-based attacks were down by about half, reaching their lowest point ever. Conversely, “Living off The Land” (LoTL) techniques, particularly through legitimate Windows processes, saw a notable 18% increase, filling the void left by scripts.
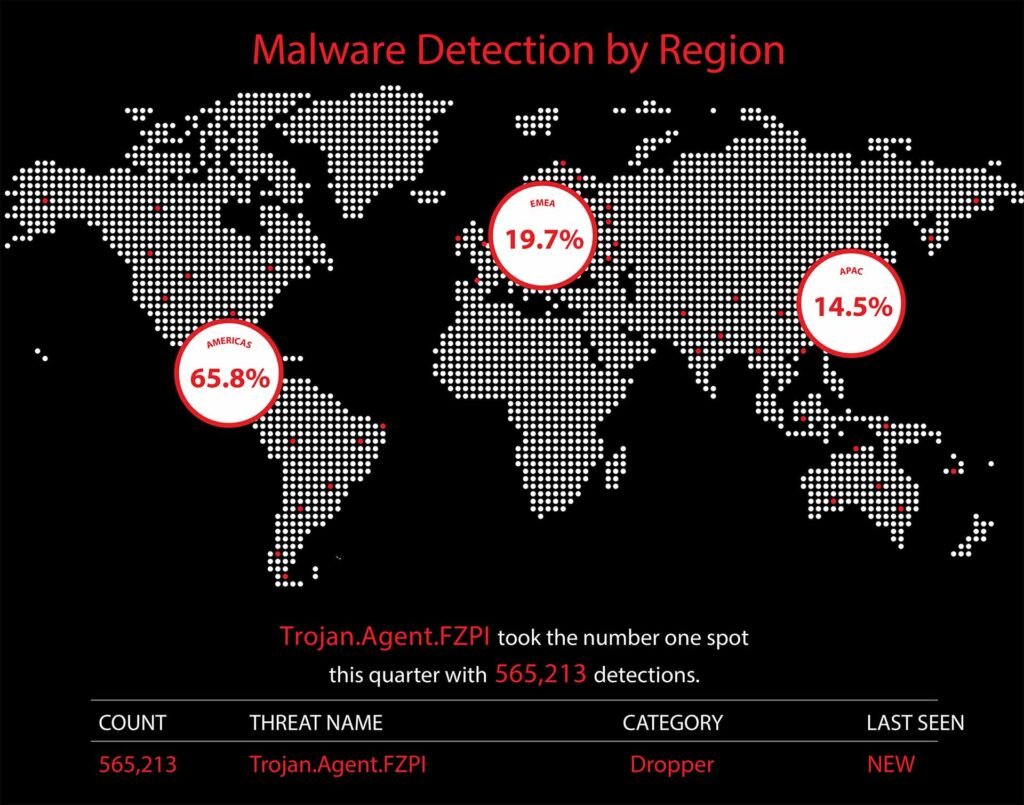
“Super Phishing” Attacks on the Rise: Trojan.Agent.FZPI, a new malicious HTML-based dropper, was the most frequently detected malware over encrypted connections. This threat combines several techniques that threat actors have employed over the past few years into a single, sophisticated phishing attachment. Organisations must implement robust TLS inspection, behavioural analysis, and endpoint protection to detect and neutralise this threat.
New Widespread Malware Identified: Application.Cashback.B.0835E4A4 emerged as the most widespread malware in Q1, impacting Chile (75.54%) and Ireland (65.43%) most significantly. The prevalence of these new variants underscores the need for region-specific defensive measures.
Network Attacks Narrow in Focus: The unique number of network signatures triggered, or known attacks detected on networks, decreased by 16% from last quarter as attackers focused on a smaller set of exploits. The network attack landscape highlights that while new exploits do emerge, attackers continue to exploit unpatched legacy vulnerabilities at scale, heavily, forcing organisations to address both fronts simultaneously.
Malware threats are continuing to emerge via email rather than the web, suggesting that threat actors are targeting users with traditional phishing techniques, as AI makes it easier to compose believable spear phishing messages. However, AI and machine learning-based tools are detecting significantly more threats at the network and endpoint perimeter in Q1 2025.








